Low fuel economy is a concern for many car owners. The increase in fuel prices has increased that concern recently. Issues inside the vehicle and non-economical driving behaviours are two major causes of the lower fuel economy. In this blog, we will discuss what issues in a vehicle can impact fuel economy and how car owners can proactively be informed via Diagnostics Trouble codes. A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a code stored in a vehicle's on-board diagnostic system (OBD) that indicates there is a problem with the vehicle's emissions, engine, or transmission. These codes are used to help diagnose and troubleshoot issues with a vehicle and are generated when the vehicle’s ECU system detects a problem or fault.
There are many potential causes of poor fuel economy in cars. Some common causes include:
- Faulty or malfunctioning oxygen sensors
- Problems with the fuel injectors or fuel pump
- Clogged or dirty air filter
- Worn or damaged spark plug
- Faulty or malfunctioning mass air flow (MAF) sensor
- Leaking or faulty fuel pressure regulator
- Malfunctioning exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
- Faulty or malfunctioning catalytic converter
In addition to these mechanical causes, poor fuel economy can also be caused by factors such as driving habits (e.g. aggressive acceleration or braking), the type of roads or terrain being driven on, and the weight or aerodynamics of the vehicle. Now let us see how the Diagnostics Trouble Code and external symptoms can help to identify one or more of the above issues.
Clogged or Dirty Air Filter
In the case of a clogged or dirty air filter, the diagnostic code that is generated will depend on the specific symptoms and effects that the clogged filter is causing. For example, if the clogged filter is causing the engine to run lean (not enough fuel), the diagnostic code that may be generated could be P0171 (System too lean, Bank 1) or P0172 (System too rich, Bank 1).
If the clogged filter is causing misfires or other issues with the ignition system, the diagnostic code that may be generated could be P0300 (Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected) or one of the specific cylinder misfire codes (P0301-P0306).
A clogged or dirty air filter may also cause other externally visible symptoms, such as:
- Reduced engine performance or power resulting in poor acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption
- Black smoke or poor idle quality
- A check engine light on the dashboard
Worn or damaged spark plug
A damaged spark plug will not be able to generate a strong enough spark to ignite the fuel inside the engine or it will not be able to generate a spark at all. This can cause the fuel to go unburned, leading to a misfire in the engine. The unburnt fuel, entering the exhaust system may also damage the catalytic converters.
Misfires can cause a variety of problems, including poor fuel economy, reduced power and acceleration, and increased emissions. P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, and P0306 are the diagnostics code generated when misfires are detected. Also, poor engine performance and black smoke from the exhaust are two major symptoms of engine misfires.
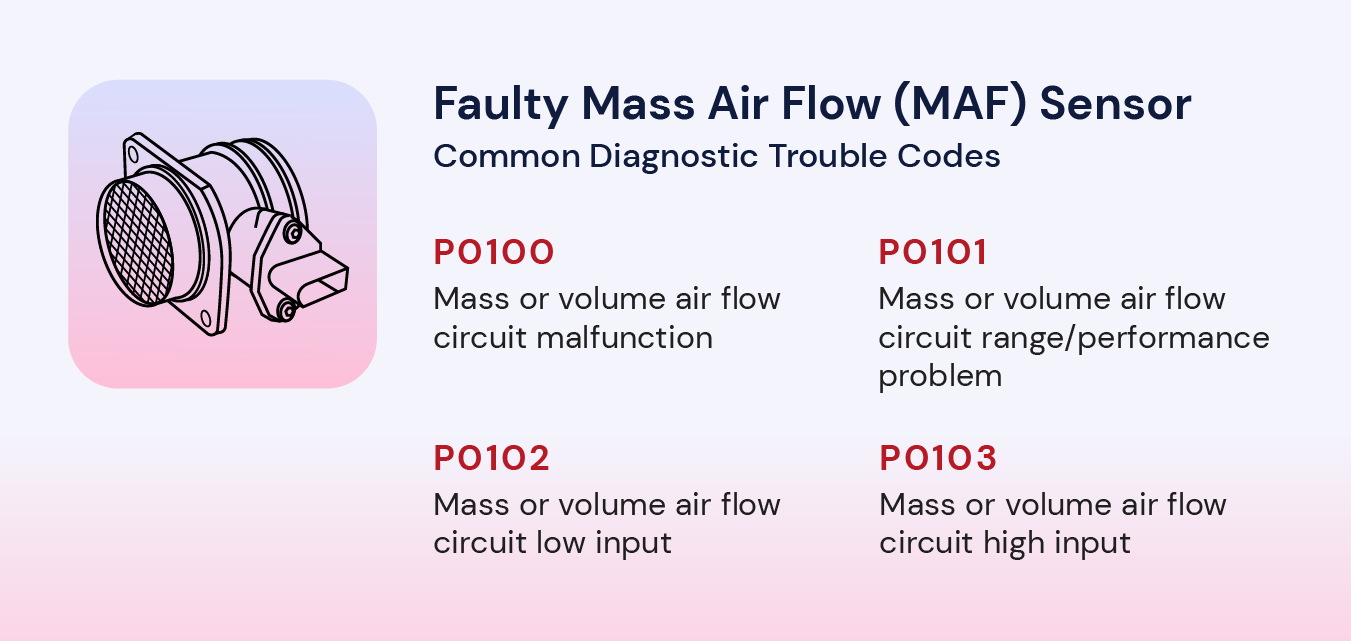
Faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The mass airflow sensor (MAF) is a device that measures the amount of air flowing into the engine and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this information to adjust the fuel-to-air ratio in the engine. If the MAF is faulty, it may send incorrect information to the ECU, causing the ECU to adjust the fuel-to-air ratio incorrectly. This can cause the engine to run lean or rich. For an engine running lean, there is not enough fuel being injected into the engine relative to the amount of air. When the engine runs lean, it can cause less power and damage to the engine. For an engine running rich, there is too much fuel relative to the amount of air in the engine and excess fuel will not be burned. This will cause higher fuel consumption for the same performance.
In the case of a faulty or malfunctioning MAF sensor, the diagnostic code generated will depend on the specific symptoms and effects the faulty sensor is causing. Some common diagnostic codes that may be generated in this case include:
- P0100: Mass or volume air flow circuit malfunction
- P0101: Mass or volume air flow circuit range/performance problem
- P0102: Mass or volume air flow circuit low input
- P0103: Mass or volume air flow circuit high input
Leaking or faulty fuel pressure regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is responsible for maintaining the correct fuel pressure for the engine to operate efficiently. If the fuel pressure regulator is faulty, it may cause the fuel pressure to be too high or too low.
If the fuel pressure is too high, it can cause fuel to be injected into the engine in larger quantities than needed. This can cause the engine to run rich
Some common diagnostic codes that may be generated due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator include:
- P0087: Fuel rail/system pressure too low
- P0088: Fuel rail/system pressure too high
- P0190: Fuel pressure sensor circuit malfunction
- P0191: Fuel pressure sensor circuit range/performance problem
Malfunctioning exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
The EGR valve is a device that helps to reduce emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine. This helps to lower the temperature and reduce the amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the exhaust gas.
If the EGR valve is faulty, it may not open or close properly, or it may become stuck in an open or closed position. This can cause problems with the engine's performance and fuel efficiency. If the EGR valve is stuck open, it can allow too much exhaust gas to be recirculated back into the engine. This can cause the engine to run lean. If the EGR valve is stuck closed, it can prevent any exhaust gas from being recirculated back into the engine. This can cause the engine to run rich.
Some common diagnostic codes that may be generated in this case include::
- P0400: Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow malfunction
- P0401: Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow insufficient detected
- P0402: Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow excessive detected
- P0403: Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) control circuit malfunction
Malfunctioning catalytic converter
A faulty catalytic converter restricts the airflow of exhaust from the engine. The build-up of exhaust gas results in the reduction of the amount of new, combustible oxygen that the engine pulls in. This throws off the engine’s air-fuel ratio and makes it run poorly.
Also, catalytic convert harmful pollutants in the exhaust gas into less harmful substances (like HC and CO to H2O and CO2). Hence a faulty catalytic converter can cause the vehicle to fail in the emission test. P0420, P0430, and P0441 are some diagnostics trouble codes generated due to a faulty catalytic converter.
About AutoWiz OBD-GPS based Fleet Management
AutoWiz OBD-GPS-based Fleet Management solution can read the above Diagnostics Trouble Codes and report it to AutoWiz mobile app and webapp. It also provides a summary, severity and information of possible component(s) failure with the diagnostic trouble code. This helps customers be aware of the exact causes of lower fuel economy and do necessary services. AutoWiz solution also reports fuel consumption for each of the trips. User can use that information to early identify the lower fuel economy of the vehicles and also to analyze the impact of the faulty component repair on the fuel economy.